Today, it’s difficult to envision a world without the Internet. More than 50 million individuals use it daily, which is growing. Effective, quality-driven web architecture has become the de-facto definition of a great product. A well-thought-out architecture with an intuitive interface ensures a seamless user experience. The web application architecture is a “skeleton” blueprint showing how application components, middleware systems, user interfaces, and databases interact.
You must realize what makes good architecture to avoid paying a lot of money to design an application. Is your design suitable for the future? Can it sustain the market or be scaled? How can one choose which features and elements to include in a web application? Continue reading to see why a skeleton for your future web application is essential.
Why is Web Application Architecture Important?
The importance of a good web application architecture cannot be overstated. It is the first step towards creating a compelling product that can provide numerous benefits to your business, including:
- Reduced costs – You will spend less on developing software than you would if you were to develop it from scratch. This will help you save for other vital investments.
- Time and effort – You can focus your time and energy on creating a suitable product rather than spending days or weeks trying to figure out how the application should work.
- User satisfaction – Users will be more satisfied with your product if it works as you intended and can use it easily and quickly.
- Customer retention – If your product is complex for users to understand or use, you will lose customers who would otherwise be willing to buy from you.
- Productivity – Your employees can spend more time on other tasks, and you can use this extra time to grow your business instead of spending it creating software for your users.
Difference Between Software Architecture and Web Application Architecture
The terms software architecture and application architecture are usually mixed up. As a result, we’d want to go through the contrasts between the two:
- Software Architecture: The architecture of the software is created with a specific objective or set of missions in mind. That goal must be carried out without interfering with the tasks of other instruments or devices. The behavior and structure of software have a considerable impact on decisions. Thus they must be rendered and created correctly for the best results.
- Web Application Architecture: An architecture created for an online application is a framework of simultaneous system elements, databases, middleware systems, user interfaces, and servers. It’s also known as the layout because it clearly outlines the interaction between the server and the client side to improve the online experience.
Components of Web Application Architecture
The web application architecture has two main components:
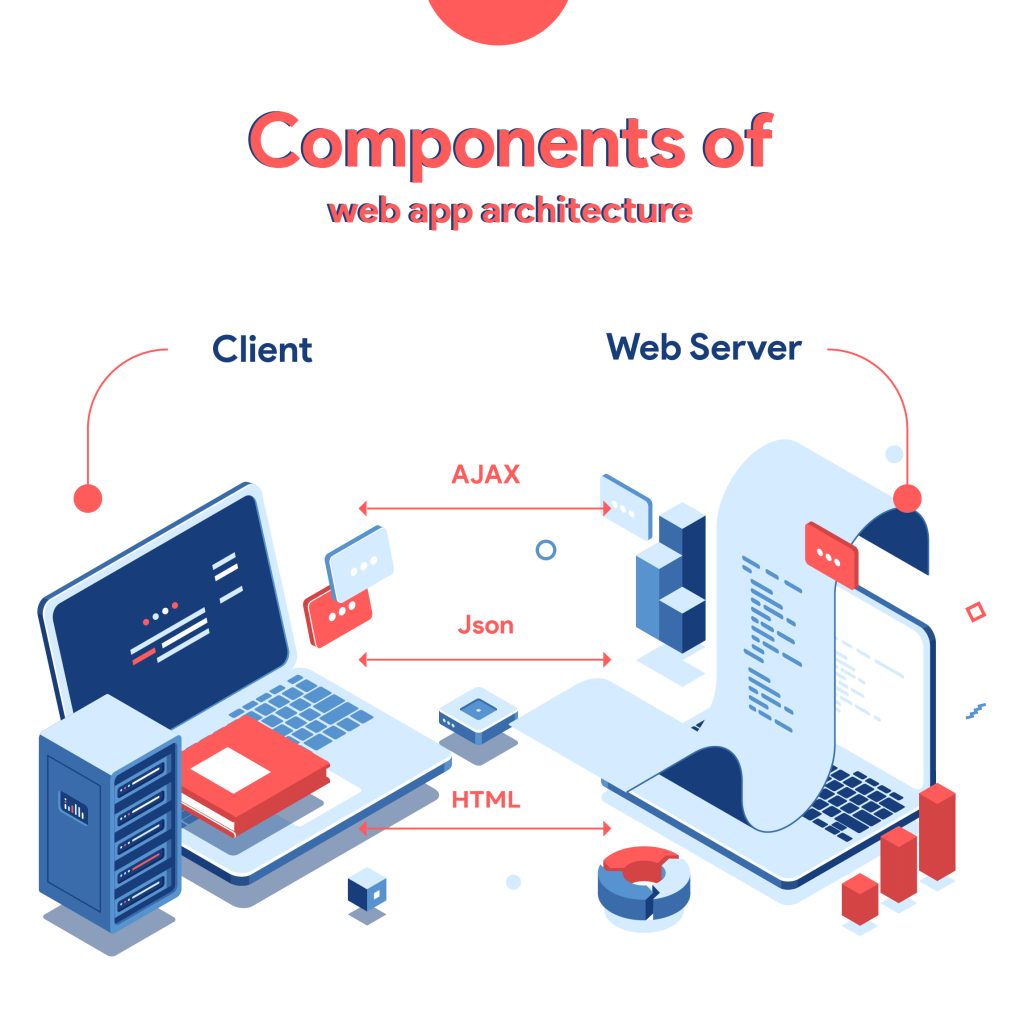
Structural Component (Server):
Client and server components make up structural web components. Client components reside in the user’s browser and interact with web application functionality. These components are usually built with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
UI & UX Component (Client):
User interface components are part of a web application’s visual interface and have no connection to the architecture. They are limited to displaying a web page and include activity logs, configuration settings, dashboards, statistics, widgets, notifications, and other features that improve the user experience.
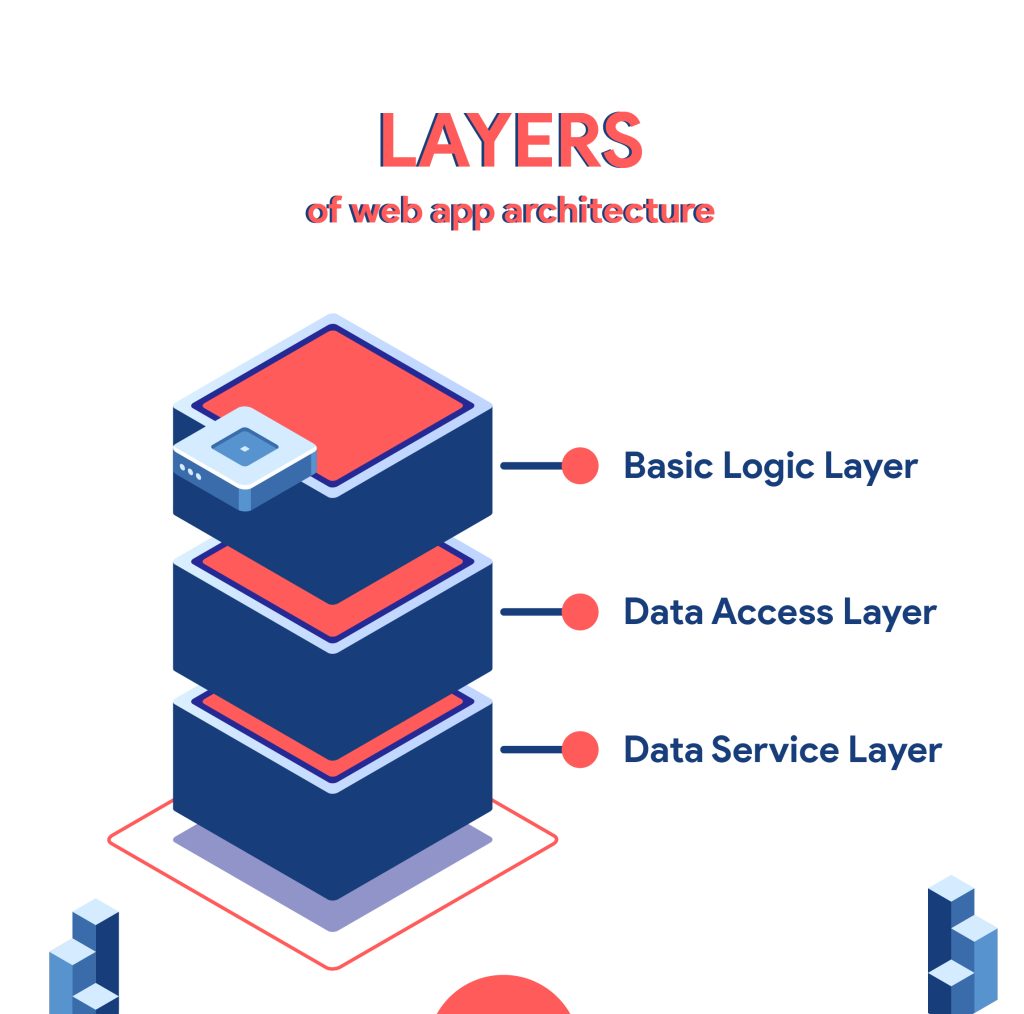
Layers of Web App Architecture
There are three main layers to web app architecture:
- Basic Logic Layer:
The basic logic layer is where all the business rules are defined. Users and developers will use this layer to define how data should be stored, retrieved, and processed.
- Data Access Layer:
The data access layer is where all the business logic and database interactions are defined. Users and developers will use this layer to define how data should be stored, retrieved, filtered, sorted, grouped, and processed.
- Data Service Layer:
Data is transferred from the server to the primary layer via the data service layer. It bridges the server and the display layer, separating business logic from client logic.
Types of Web Application Architecture
It’s usually a good idea to choose the best architecture for your app while keeping many things in mind, such as app logic, features, functionality, and business requirements. The objective of your product as a whole is defined by its architecture. A few common ones are:
Single page application:
SPAs load a single web page and refresh the needed data on the same page with dynamically updated information rather than loading a new page. The remainder of the website is unaffected.
Multi-page application:
A multi-page application (MPA) is an app that loads all of its content from multiple HTML files. This type of architecture may be used for applications with large data sets, such as e-commerce or enterprise apps.
Microservices:
Microservices architecture is a software design pattern in which applications are composed of small, loosely coupled services. These services communicate with each other using well-defined APIs.
Serverless:
Serverless architecture is an application architecture in which a cloud service handles the functions that are not required to be run on a server. This type of architecture may be used for applications with large data sets.
RAD stack:
A rapid Application Development stack is a set of tools and technologies used to build web applications. The RAD stack is designed to be used by developers who are unfamiliar with the technologies involved and do not require any knowledge of programming languages.
Progressive web app architecture:
This is a type of application architecture that Google first developed. It is an app that can be installed on any device and will have the same user experience. The PWA architecture is best suited for applications that require a high level of user engagement and interactivity, such as chat apps.
Bottom Line
The architecture of online applications, like the Internet itself, is constantly changing. During the era of Web 1.0, the fundamental model of web application architecture appeared. However, it took on its current form with the introduction of Web 2.0 and Web 3.0. The model and type of web application architecture one picks significantly impact an online application’s robustness, responsiveness, security, and other characteristics. As a result, before beginning development, spend time examining all requirements, goals, and options.
The architecture of a modern web application is inextricably linked to its success. Maintaining changing requirements is complex, and even a tiny blunder can cost your product’s life. A competent and experienced architect is needed to design a modern web application architecture that understands the limitations and challenges that come with it.